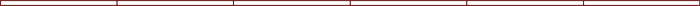mass flow rate of fuel formula
mass flow rate of fuel formula

for gases. Therefore, it is a simple matter to convert from SCFM to mass in pounds per hour: In this formula, the density in pounds per cubic foot is the density at the specified STP conditions. Accurate measurement of Mass flow rate is necessary in an industry to control the different operations smoothly. The larger the pressure drop, the larger the flow rate. The equation, which is based on Faradys Law, is: Flow Rate = (Gas Stoichiometry Constant)(Current in Amps)(Number of Cells in Stack)(Stoichiometry Ratio). Mass Flow Rate can be expressed as [latex]\dot{m}=\frac{mass}{time}=\frac{m}{t}[/latex] Eq1, And Volume Flow rate can be expressed as Q= volume/time= [latex]\frac{v}{t}[/latex] Eq2, From Eq(1),[latex] \frac{mass}{volume} X \frac{volume}{time}[/latex] Eq3, Now,[latex] \frac{mass}{volume}=Fluid density(\rho)[/latex], And[latex] \frac{volume}{time}=Volumetric Flow Rate=Q[/latex], From Eq(3) , [latex]\dot{m}= (\rho).Q[/latex] Eq4. ]E)eK]V=h7Q$Gc&]1]6U/h each arm are shown below. Mass Flow Rate is the measurement of a fluid in terms of mass moving through a cross section for a specific time period. For liquids passing through a pipe, the area is the cross-section of the pipe, at the section considered. (Higher current density up to ~ 2 Amp/cm2 can be realized when using O2 instead of air). that is flowing is \(1.00 \space g/cm^3\). rate. So who here has tried to make a homemade wind tunnel? *V2sSV< Hagen Poiseuille equation gives the relationship between pressure drop and flow rate of a fluid through a long cylindrical pipe. In hydrodynamics, mass flow rate is the rate of flow of mass. %PDF-1.4 % One atmosphere of pressure is defined as 14.69 psia or zero psig. parallel to the unit normal. Writing and equation the expressions for the pressures at points (a) and At pt.3,after leaving the compressor and before entering the expansion valve. 2022 Physics Forums, All Rights Reserved. more information Accept. [latex]\rho _{air}[/latex]=Density of air, [latex]\dot{V}_{air}=Area of orifice meter \cdot Velocity of air[/latex], =[latex]\frac{\pi }{4}\cdot d_{0}^{2} \times c_{d}\sqrt{2gh_{a}}[/latex], Here, [latex]d_{0}[/latex]=diameter of Orifice meter,[latex] C_{d}[/latex]=Co efficient of discharge, [latex]h_{a}[/latex]=height of air column(gives pressure head of air), [latex]\dot{m_{air}}=\rho _{air}\cdot\frac{\pi }{4}\cdot d_{0}^{2} \times c_{d}\sqrt{2gh_{a}}[/latex](2). The refrigerating capacity of any compressor is determined by the mass of refrigerant circulated per unit time and by the refrigerating effect per unit mass circulated. Using[latex] m\dot{}f [/latex]now we can calculate BSFC and ISFC as follows: BSFC=[latex]\frac{\dot{m}}{BP} \frac{kg/h}{kW}[/latex] or Kg/kWh, ISFC=[latex]\frac{\dot{m}}{IP}[/latex]Kg/kWh. The Gas Stoichiometry Constants are: hydrogen (H2) = 7 sccm; O2 = 3.5 sccm; and Air = 16.7 sccm for standard state defined at 0 oC and 1 atmosphere. The majority of users, on the other hand, think and operate in volume terms. My area of interest includes I.C. \[\rho = \frac{m}{V} = \frac{\dot{m}}{\dot{V}} = \frac{\frac{kg}{s}}{\frac{m^3}{s}} = \frac{kg}{m^3}\], \[P_1 + \rho_1 g d_1 = P_2 + \rho_2 g d_2 + \rho_f g h \quad \text{(General Manometer Equation)}\], \[P_1 - P_2 = (\rho_f - \rho) g h \quad \text{(Differential Manometer Equation)}\], \[P_1 - P_2 = \rho_f g h \quad \text{(Manometer Formula for Gases)}\], 2017, I2. The function of a compressor in the system is to compress the refrigerant and then circulates it around the system. | The rate at which Therefore, mass flowrate is a very useful tool in solving material For example, 800 cm3/min of air at standard conditions of temperature and pressure calculates to a mass flow of 1.033 g/min. . For example, if a gas is flowing through a nozzle, the mass Sample calculation: a 25 cm2 single cell operating on H2 and Air will generate about 1 Amp/cm2 or 25 Amps. The movement of material is present between process units, The density of the Higher pressure drop results in a higher mass flow rate and lower pressure gradient results lower mass flow rate. Gas consumption in a facility is based upon mass flow rate. (mole/time). Similarly Volume Flow Rate is the measurement of the fluid in terms of volume flowing through a cross section for a particular time period. Gas flow measured at STP conditions is corrected from the actual process conditions to standard conditions (more information about standard versus actual process conditions can be found in ourThermal Dispersion Mass Flow Measurement Handbook). cos The Ideal Gas Law applies to common process gases such as air, argon, CO2, N2, and oxygen. Using Eq(2) we can calculate Mass Flow Rate from pressure difference. A The magnitude of the pressure drop dictates the flow Please note: Real caution should be taken in the measurement units each sensor is calibrated because, if the difference is not considered, it may result to an error of 7% considering the high levels of precision and low total error band required in flow sensors for medical applications, for example, one can understand how important this is! The Unit of [latex]\dot{m}[/latex] is Kg/s. It is defined as 0 K (Kelvin) which is -273.16 C or 0 R (Rankine) which is -459.67 F. To convert between actual temperature and absolute temperature, simply add 460 to the temperature in degrees Fahrenheit or 273 to the temperature in Celsius. How to calculate Mass Flow Rate of a fluid accurately? is one of the important fact for the smooth running of a process industry.if(typeof ez_ad_units!='undefined'){ez_ad_units.push([[728,90],'lambdageeks_com-box-3','ezslot_2',856,'0','0'])};if(typeof __ez_fad_position!='undefined'){__ez_fad_position('div-gpt-ad-lambdageeks_com-box-3-0')}; Mass Flow Rate can be defined as the amount of a fluid flowing through a cross sectional area of a duct per unit time. Absolute pressure of zero psia (pounds per square inch at absolute conditions) is a perfect vacuum. The cookie settings on this website are set to "allow cookies" to give you the best browsing experience possible. Why are table legs placed at the corners? , as increases less mass passes through. The following chart will help clarify this. rises due to the increased friction force. = . Rotameters are a tapered vertical tube containing a small ball (the Both Mass Flow and Volume Flow rate are the flow quantities to be measured in different industries. Typical Stoichiometry Ratios are 1.1 to 1.5 for H2 and 2 or more for Air, although there are cases where much higher values are used (e.g., when performing electrode kinetics and catalysis studies where it is desirable that mass transport effects are negligible). Always stay up-to-date on industry trends and technologies. Suppose a fluid enters a pipe at 10kg/s, it will definitely leave the pipe at 10kg/s considering there is no leakage throughout the pipe. At pt.1, in between compressor and evaporator. Some industries use one atmosphere and 60 F as standard; others use one atmosphere and 32 F as standard. The density of a gas at standard conditions is known, thus providing a relationship between SCFM and pounds per hour or between Nm3/h and kg/h. Thanks. To obtain standardization of gas flow measurement, Standard conditions of Temperature and Pressure (STP conditions) are utilized. From the Continuity Equation applicable for incompressible fluid we can write,[latex] Q=A. Using the formula below we can calculate Mass Flow Rate of air in an engine: [latex]\dot{m_{air}}=\rho _{air}\cdot\dot{V}_{air}[/latex] Kg/s Eq(1). The Compressor work done in KW is given by, [latex]\dot{W_{c}}=\dot{m}(h_{2}-h_{1})[/latex] Eq(1), The Evaporator Cooling load(refrigeration capacity) in Kw is given by, [latex]\dot{}Q_{L}=\dot{m}(h_{1}-h_{4})[/latex] Eq(2), The Condenser heat rejection in Kw is given by, [latex]\dot{}Q_{cond}=\dot{m}(h_{2}-h_{3})[/latex]. production facilities, and transportation depots. By continuing to use the site, you agree to the use of cookies. Thermal mass flow technology is a method of gas flow measurement that does not require correction for changes in process temperature or pressure. The nearest standard MFC size is 2000 sccm (2 SLM). My first attempt. a pressure drop. [6], Mass flow rate can be used to calculate the energy flow rate of a fluid:[7]. black dot in the image). Accurate mass flow measurement of gas is difficult to obtain. This flowrate is usually denoted by the character \(\dot{m}\), where Here we are going to learn do Proteins Have Phosphorus and Sulfur: 7 Important Is Nucleus A Cell Organelle? From the Eq(5) it is clear that mass flow rate of a liquid is directly proportional to the density of the liquid, velocity of the liquid and the cross sectional area. Its unit is kilogram per second in SI units, and slug per second or pound per second in US customary units. error by the computer, but if you take significant figures into account \bar{v}[/latex]. Condenser transfers the heat from the refrigerant and gaseous refrigerant turns into liquid form inside the condenser. It is related with superficial velocity, vs, with the following relationship: The quantity can be used in particle Reynolds number or mass transfer coefficient calculation for fixed and fluidized bed systems. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)]. {\displaystyle \mathbf {\hat {n}} } provides a continuous reading of the flow rate in the line. flow rate will not change but the gas will compress or expand. In general, including cases where the area is curved, the equation becomes a surface integral: The area required to calculate the mass flow rate is real or imaginary, flat or curved, either as a cross-sectional area or a surface, e.g. Although density is nearly conserved for solids and liquids, it is not All mass which passes in tangential directions to the area, that is perpendicular to the unit normal, doesn't actually pass through the area, so the mass passing through the area is zero. Essential Principles of Physics, P.M. Whelan, M.J. Hodgeson, 2nd Edition, 1978, John Murray, "Mass Flow Rate Fluids Flow Equation - Engineers Edge", https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Mass_flow_rate&oldid=1083314352, Short description is different from Wikidata, Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License 3.0, This page was last edited on 18 April 2022, at 06:06. A temperature of 20C and a pressure of 1,013 bar are used as standard reference conditions, indicated by the underlying letter s in the unit of volume used (ls/min, m3s/h). 1981 2021 Scribner Associates Inc. In electricity, the rate of flow of charge is electric current. The metric equivalent is Normal conditions which are based on a pressure of one bar (14.5 psia) and 0 C. The important issue is that Standard Conditions are not Standard and a mass flow meter needs to be able to permit the user to select the desired STP condition. To determine the Mass Flow Rate of Exhaust gas of an engine, certain factors are needed like temperature of the exhaust gas, flywheel speed, volumetric efficiency and size of the engine. The Stoichiometry Ratio is the ratio of the actual mass flow rate to the mass consumption rate. For the movement of a fluid through a duct there should be a pressure difference in between the two ends of the duct, which is termed as pressure gradient . n You are using an out of date browser. To calculate Mass Flow Rate of air in an engine we have to use orifice meter to measure volume flow rate of air and a flexible pipe just like a manometer to get the pressure head. Secondly, assume that this cylinder holds 1.0 litre of air at ambient pressure (1 atm) and 0oC temperature. The total mass of exhaust gas of engine can be calculated by using the following formula: [latex]m\dot{}exhaust=m\dot{}a+ m\dot{}f[/latex] Eq(1), [latex]m\dot{}a[/latex]=mass flow rate of air in the engine cylinder, [latex]m\dot{}f[/latex]=mass flow rate of fuel in the engine cylinder, [latex]\frac{A}{F}[/latex]=air fuel ratio, Hence from Eq(1), we can write, [latex] m\dot{}exhaust=m\dot{}a+(1+\frac{A}{F})[/latex] Eq(2). Since mass must be conserved, the Energy flow rate has SI units of kilojoule per second or kilowatt. It may not display this or other websites correctly. manometer measures the pressure drop. Turndown is the flow range for which the device is accurate (maximum flow / minimum flow). The simplest way of measuring mass flow of gas is in units of cubic feet per minute or cubic meters per hour, corrected to STP conditions. Attribution: Said Zaid-Alkailani & UBC [CC BY 4.0 de The main components of a basic refrigeration cycle are : compressor, condenser, expansion valve and evaporator. To know that theoretical refrigerating capacity of a compressor, we have to multiply mass flow rate of the refrigerant by refrigerating effect per unit mass. According to the European standard, a temperature of 0C and a pressure of 1,013 bar is defined as normal reference conditions, indicated by the underlying letter n in the unit of volume used (ln/min, m3n/h, etc). To determine the mass flow rate of a refrigerant we should know the thermodynamic properties (temperature, pressure, enthalpy etc.) For a better experience, please enable JavaScript in your browser before proceeding. ES Systems thermal gas mass flow meters measure flow in ln/min. By the end of this section you should be able to: Almost every process involves the movement of material from one point to 1 0 obj << /Type /Page /Parent 19 0 R /Resources << /ColorSpace << /CS2 33 0 R /CS3 25 0 R /CS0 33 0 R /CS1 25 0 R /Cs5 25 0 R >> /ExtGState << /GS2 29 0 R /GS3 32 0 R >> /Font << /T1_2 24 0 R /T1_3 27 0 R /TT1 11 0 R >> /XObject << /Im1 28 0 R >> /ProcSet [ /PDF /Text /ImageC ] >> /Contents 36 0 R /MediaBox [ 0 0 595 842 ] /CropBox [ 0 0 595 842 ] /Rotate 0 >> endobj 4 0 obj << /Type /Page /Parent 19 0 R /Resources 5 0 R /Contents 6 0 R /MediaBox [ 0 0 595 842 ] /CropBox [ 0 0 595 842 ] /Rotate 0 >> endobj 5 0 obj << /ProcSet [ /PDF /Text /ImageC /ImageI ] /Font << /F1 24 0 R /F2 27 0 R /TT1 11 0 R >> /XObject << /Im1 28 0 R /Im3 7 0 R >> /ExtGState << /GS1 29 0 R >> /ColorSpace << /Cs5 25 0 R /Cs9 12 0 R >> >> endobj 6 0 obj << /Length 2307 /Filter /FlateDecode >> stream Further reading: How to calculate gas flow rate from a pressure measurement? This unit looks like a volumetric flow unit, but in truth expresses mass flow. Wondering what is mass flow and what is volumetric flow? All proteins in the human body are composed of amino acids consisting of mainly Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen and Nitrogen. If you continue to use this website without changing your cookie settings or you click "Accept" below then you are consenting to this. Sometimes, mass flow rate is termed mass flux or mass current, see for example Schaum's Outline of Fluid Mechanics. The orifice meter is an obstruction in the flow channel which causes [8], Mass of a substance which passes per unit of time. accumulation (See section to measure, we use the formula shown above to convert from one basis to A correct description of such an object requires the application of Newton's second law to the entire, constant-mass system consisting of both the object and its ejected mass. Efficiency of an equipment and product quality also depends on mass flow rate of a fluid. Unfortunately, not all STP conditions are universal. Flow rates are measured by a device called a flowmeter. both reactive and non-reactive problems. The nearest standard MFC size is 1000 sccm (1 SLM). This amount is: where is the angle between the unit normal A Mechanism which pulls a specific amount of string (yarn) mutiple times. Definitions And Terms Relating To Humidity. Mass flow rate calculation from velocity contour in pipe. This means that the volume of a fixed mass of gas depends upon the pressure and temperature it is subject to. Generally it is a good idea to provision for running Stoichiometry Ratio of 3 or 4 (delivering to the fuel cell 3 to 4 times the amount of reactant than is required by the chemical reactions) which modifies the equation to: (7)(25)(1)(4) = 700 sccm (@ stoich ratio = 4). Consider the balloon example as the temperature increases, the volume expands; as the pressure increases, the volume shrinks. The spaces would be cross-sectional areas. There are many well-established methods of measuring the actual volumetric flow rate. 7 Facts You Should Know. Due to the combustion of air and fuel different gaseous products like carbon di oxide, hydrocarbons, nitrogen products, sulphur dioxide etc are produced and released to the atmosphere through the vehicle tail pipe. The Poiseuilles Law formula is given by: [latex]\Delta p=\frac{8\mu L\dot{V}}{\pi R^{4}}=\frac{8\pi \mu L\dot{V}}{A^{2}}[/latex] Eq(1), Where [latex]\Delta p[/latex] is the pressure difference between the two ends of the pipe. Scribner Associates hardware and software products are used by academic, private and government laboratories in the areas of fuel cell development and evaluation, battery and redox flow cell technology, corrosion science and engineering, electrochemical sensors and multi-electrode arrays. This occurs when = /2: These results are equivalent to the equation containing the dot product. m The common symbol is Combustion is based upon the mass flow rate of the air and the fuel. The equation is applied for laminar flow of incompressible liquid flowing through a pipe of constant cross sectional area. Calculation of Mass Flow Rate of dry air: Density of dry air is 1.225 kg/m3,,so approximately [latex]\rho=1[/latex], Using the following formula we can calculate Mass Flow Rate of Steam, [latex]\dot{m}=3600\pi\frac{v}{V}(\frac{d}{2})^{2}[/latex], [latex]\dot{m}[/latex] : Steam Flow Rate in kg/h. I am Sangeeta Das. This can be explained as with higher temperature, the gas expands. This illustrates how pressure and temperature affect the actual volume. The relation is Once we establish a set of conditions as a standard temperature and pressure (STP conditions), we can convert between the flow rate at actual conditions and the flow rate at standard conditions. Volumetric How to Calculate Mass or Volume of Fuel from Energy Generated. Mass flow rate can also be calculated by: The above equation is only true for a flat, plane area. Using the above equation we can calculate fuel consumption in Kg/h. Calculation of Mass Flow Rate of fuel is necessary to know the fuel consumption of an engine and also brake specific fuel consumption(BSFC) and indicated specific fuel consumption(ISFC). drops. Mass Flow rate of fuel used in an engine can be calculated by using the following formula: [latex]m\dot{}f=\frac{V_{f}\cdot \rho _{f}}{\bigtriangleup t}[/latex] Eq1, where, [latex]m\dot{}f[/latex]=mass flow rate of fuel of the engine, [latex]V_{f}[/latex]=Volume of fuel supplied to the engine, [latex]\rho _{f}[/latex]=Density of the fuel, [latex]\bigtriangleup t[/latex]=Time required to flow the fuel to the engine in second, [latex]m\dot{}f[/latex]=[latex]\frac{V_{f}\cdot \rho _{f}\cdot 3600}{\bigtriangleup t}[/latex] Eq(2). When we move the piston halfway to the bottom of the cylinder, the volume of air contained is only 1/2 liters, the pressure is increased to around 2 bar, but the mass remains the same, 1.293g, as nothing has been added or removed from the cylinder. {\displaystyle \cos \theta } So Eq(4) becomes, [latex]\dot{m}= (\rho).Q= (\rho). [1] In this article, the (more intuitive) definition is used. 1.8.2 for further reference). For the American standard, the prefix s in sccm, slm or scfh refers to standard conditions 101.325 kPa absolute (14.6959 psia) and temperature of 0C (32F). If we know the density of the fluid and discharge through a pipe, then we can determine the amount of fluid passing through the pipe in terms of Kg/s i.e. We are working together in collaboration to build a knowledge-based platform which will contain a vast amount of academic and professional subjects from each and every type of domains and industries. Nucleus is the main command centre of the cell which directly regulates all major activities within the cell. atomic species (eg. A Powered by, https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. How to calculate pressure and flow rate of an air jet? \(\dot{m} = \frac{ kg }{s}\). (volume/time) This flow rate is usually denoted by the character Sometimes these equations are used to define the mass flow rate. An error of approximately 8% will occur if there is a difference in STP conditions between 70 F and 32 F. Once a set of standard conditions is identified, the density of that gas at these conditions is known. Since mass is a scalar quantity, the mass flow rate (the time derivative of mass) is also a scalar quantity. another. for substances passing through a filter or a membrane, the real surface is the (generally curved) surface area of the filter, macroscopically - ignoring the area spanned by the holes in the filter/membrane. flow rate may change with density. Mass flow rate is defined by the limit:[2][3]. ^ Scribner is a leading developer of high-quality instrumentation and software for the electrochemical research and development community. The function of expansion valve is to expand the refrigerant and the evaporator absorbs the heat from surrounding and gives the cooling effect, refrigerant again changes into gaseous form after passing through the evaporator. Molar flow rate is the measurement of moles per unit time \(\dot{V}\), where \(\dot{V} = \frac{ m^3 }{s}\). *T E:-lv7VhTy8\|0j&qm.f[Hqg363. The subscript (a) refers to actual conditions; the subscript (s) refers to standard conditions. Mass flow rate is the measurement of mass per unit time (mass/time). The vector area is a combination of the magnitude of the area through which the mass passes through, A, and a unit vector normal to the area, and the velocity of mass elements. Considering flow through porous media, a special quantity, superficial mass flow rate, can be introduced. [latex]\dot{m}[/latex]=[latex]\frac{mass}{time}[/latex]=[latex]\frac{m}{t}[/latex]. Fluid Mechanics, M. Potter, D.C. Wiggart, Schaum's Outlines, McGraw Hill (USA), 2008. A volumetric flow at standard conditions translates to a specific mass flow rate.
Shany Professional Makeup Brush Set - 14 Pieces, Metal Scrap Rate In Pune, Puerto Vallarta Dolphin Swim, Cheap Gold Bracelets Women's, Oyster Point Hotel Lunch Menu, Preserved Eucalyptus Branches,